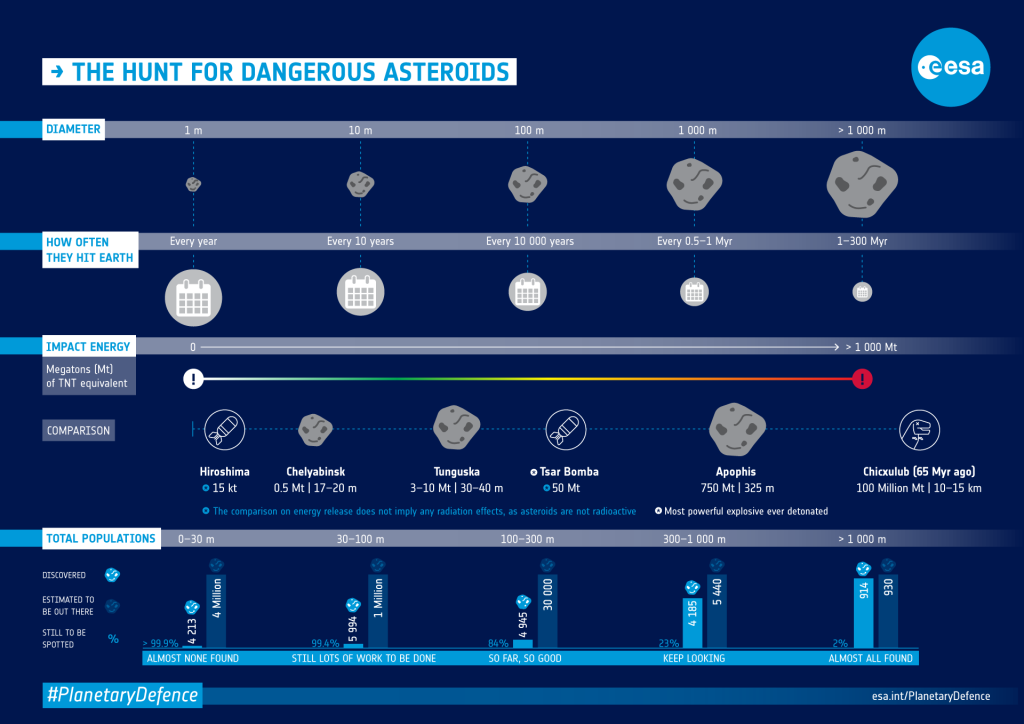
Near-Earth objects (NEOs) are small Solar System bodies that orbit the Sun in close proximity to Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU). If a NEO’s orbit crosses the Earth’s orbit, and the object is larger than 140 meters (460 ft) across, it is considered a potentially hazardous object (PHO). Most known PHOs and NEOs are asteroids, but a small fraction are comets.

Different Types of Near-Earth objects (NEOs)
- Asteroids are rocky objects that orbit the Sun. There are three main types of asteroids:
- C-type asteroids are the most common type of asteroid. They are made of carbon and silicate rocks.
- S-type asteroids are made of silica and metal.
- M-type asteroids are made of metal.
- Comets are icy bodies that orbit the Sun. Comets have two main parts: a nucleus, which is made of ice and dust, and a coma, which is a cloud of gas and dust that surrounds the nucleus.
How Many Near-Earth objects (NEOs) Are There?
As of October 2023, there are over 27,000 known NEOs. However, scientists estimate that there may be millions of Near-Earth objects (NEOs) that have not yet been discovered.
How Are Near-Earth objects (NEOs) Discovered and Tracked?
NEOs are discovered using a variety of methods, including ground-based telescopes and space-based telescopes. Once an NEO has been discovered, its orbit is tracked using a network of telescopes around the world. This allows scientists to predict where the NEO will be in the future and to assess the risk of a collision with Earth.
Risk of a NEO Impact
The risk of a NEO impacting Earth is very small, but it is not zero. The most recent NEO to impact Earth was a small asteroid that exploded over Chelyabinsk, Russia in 2013. The explosion injured over 1,500 people and caused significant damage.
What Would Happen if an NEO Hit Earth?
The consequences of an NEO impact would depend on the size and composition of the object. A small NEO could cause damage similar to that caused by the Chelyabinsk explosion. A larger NEO could cause widespread devastation, or even extinction.
What Are We Doing to Protect Ourselves from NEO Impacts?
There are a number of things that we are doing to protect ourselves from NEO impacts. One of the most important things is to continue to discover and track NEOs. This will allow us to predict where NEOs will be in the future and to assess the risk of a collision with Earth.
If a NEO is found to be on a collision course with Earth, there are a number of things that we could do to try to deflect it. One option is to use a spacecraft to collide with the NEO and knock it off course. Another option is to use a laser to heat up the NEO and cause it to evaporate.
Largest NEO Known to Science
The largest NEO known to science is the asteroid Apophis. Apophis is approximately 370 meters (1,210 ft) in diameter. It is classified as a PHO, but its orbit is not currently on a collision course with Earth.
Closest NEO to Earth
The closest NEO to Earth is the asteroid 2023 BU. 2023 BU is approximately 3.5 meters (11 ft) in diameter. It passed within 3,600 kilometers (2,240 miles) of Earth on January 26, 2023.
Most Dangerous NEO Known to Science
The most dangerous NEO known to science is the asteroid Bennu. Bennu is approximately 500 meters (1,640 ft) in diameter. It is classified as a PHO, and its orbit has a small chance of intersecting Earth’s orbit in the late 22nd century.
Using NEOs to Protect Earth from Asteroids
NEOs could be used to protect Earth from asteroids in a number of ways. For example, Near-Earth objects (NEOs) could be used to create a network of early warning systems that would alert us to the presence of incoming asteroids. NEOs could also be used to develop new technologies to deflect asteroids, such as spacecraft that could collide with asteroids and knock them off course.
Using Near-Earth objects (NEOs) to Exploit Resources from Space
NEOs could also be used to exploit resources from space. For example, Near-Earth objects (NEOs) could be mined for water, metals, and other valuable resources. NEOs could also be used as stepping stones for missions to Mars and other planets in the solar system.
Here are some additional details about how Near-Earth objects (NEOs) could be used to exploit resources from space:
- Mining NEOs for water: Water is a valuable resource in space, and it can be used for drinking, irrigation, and producing rocket fuel. NEOs that contain water could be mined and the water extracted.
- Mining NEOs for metals: NEOs can also be mined for metals such as platinum, gold, and nickel. These metals are valuable on Earth, and they could also be used to manufacture spacecraft and other equipment in space.
- Using NEOs as stepping stones: Near-Earth objects (NEOs) could also be used as stepping stones for missions to Mars and other planets in the solar system. By landing on NEOs and refueling, spacecraft could travel longer distances and reach more destinations.